10 Surprising Facts About Neurogenic Bladder That You Need to Know
2024-06-20 / RG STONE HOSPITAL / Female Urinary Incontinence
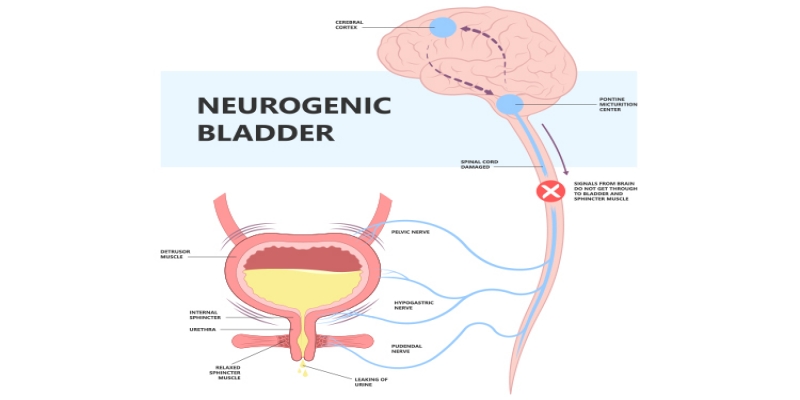
Neurogenic bladder is a condition that affects the bladder's ability to store and empty urine properly due to a neurological disorder or injury. It can be a challenging condition to manage, but understanding it can help improve the quality of life for those affected. Here are ten surprising facts about neurogenic bladder that you need to know.
-
Neurogenic Bladder Can Have Various Causes Neurogenic bladder is not a single condition but a symptom of an underlying neurological disorder or injury. Some common causes include spinal cord injuries, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, stroke, spina bifida, and diabetic neuropathy. These conditions can disrupt the normal communication between the brain, spinal cord, and bladder, leading to difficulties with bladder control.
-
It Can Cause Either Overactive or Underactive Bladder Symptoms Depending on the location and severity of the neurological injury or disorder, a neurogenic bladder can manifest as either an overactive bladder or an underactive bladder. An overactive bladder is characterized by sudden, frequent urges to urinate, and sometimes leakage. On the other hand, an underactive bladder may cause difficulty fully emptying the bladder, leading to urinary retention and the need for catheterization.
-
Early Diagnosis and Treatment are Crucial Prompt diagnosis and treatment of neurogenic bladder are essential to prevent potential complications, such as urinary tract infections, bladder stones, and kidney damage. If left untreated, the bladder can become stretched and inefficient, leading to further complications and a decreased quality of life.
-
There Are Different Types of Neurogenic Bladder Neurogenic bladder can be classified into several types based on the underlying neurological condition and the bladder's behavior. The main types include:
-
Overactive Neurogenic Bladder: Characterized by uncontrolled bladder contractions and urinary incontinence.
-
Underactive Neurogenic Bladder: Characterized by an inability to empty the bladder, leading to urinary retention.
-
Mixed Neurogenic Bladder: A combination of overactive and underactive bladder symptoms.
-
Treatment Options Vary Based on the Type and Severity The treatment approach for neurogenic bladder depends on the type, severity, and underlying cause. Common treatment options include:
-
Medications: Anticholinergics, alpha-blockers, and botulinum toxin injections can help manage bladder symptoms.
-
Intermittent Catheterization: Using a catheter to drain the bladder at regular intervals can prevent urinary retention and potential complications.
-
Bladder Retraining: Techniques such as timed voiding and pelvic floor muscle exercises can help improve bladder control.
-
Surgery: In some cases, surgical interventions like bladder augmentation or urinary diversion may be necessary.
-
Lifestyle Modifications Can Help Manage Symptoms In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing neurogenic bladder symptoms. These may include:
-
Dietary changes: Limiting fluid intake, avoiding bladder irritants like caffeine and alcohol, and following a timed voiding schedule.
-
Pelvic floor exercises: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can improve bladder control.
-
Bladder retraining: Gradually increasing the time between bathroom visits can help retrain the bladder.
-
Neurogenic Bladder Can Affect Quality of Life Neurogenic bladder can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, both physically and emotionally. Bladder leakage, frequent urination, and the need for catheterization can lead to social isolation, depression, and reduced self-esteem. Proper management and support are crucial for maintaining overall well-being.
-
It Requires Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustments Neurogenic bladder is a chronic condition that requires ongoing monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals are essential to assess the effectiveness of the current treatment and make any necessary changes to ensure optimal bladder function and prevent complications.
-
Complications Can Be Serious If left untreated or improperly managed, neurogenic bladder can lead to serious complications, including:
-
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Incomplete bladder emptying can increase the risk of UTIs, which can further damage the kidneys if left untreated.
-
Bladder Stones: Stagnant urine in the bladder can lead to the formation of bladder stones, which can cause pain, bleeding, and obstruction.
-
Kidney Damage: Chronic urinary retention and high bladder pressures can lead to kidney damage and even kidney failure if not addressed promptly.
-
Support and Education Are Essential Living with neurogenic bladder can be challenging for the individual and their caregivers. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and educational resources can help individuals and their families better understand and manage the condition, cope with the emotional challenges, and improve overall quality of life.
Neurogenic bladder is a complex condition that requires proper management and ongoing monitoring. By understanding these surprising facts, individuals affected by neurogenic bladder can take proactive steps to manage their symptoms, prevent complications, and maintain a good quality of life.
Categories
Hernia Repair
Appendicitis
Piles
Urological Treatment
Hernia treatment
Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Gall Bladder Stone
Urinary / Kidney Stone
Vitamins
Indian Health Care System
Exercise
Obesity
Female Urinary Incontinence
Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery (SILS)
Kidney Cancer
Bladder Cancer
Ovarian cancer
Nephrology
Bariatric Surgery
Kidney Function Test
Female Urology
Radiation Therapy
Alcoholic Fatty Liver
Liver disease
Gastroenterology
Kidney Disease

