The Ultimate Guide to Recognising Overactive Bladder Symptoms
2025-03-17 / RG STONE HOSPITAL / Female Urology
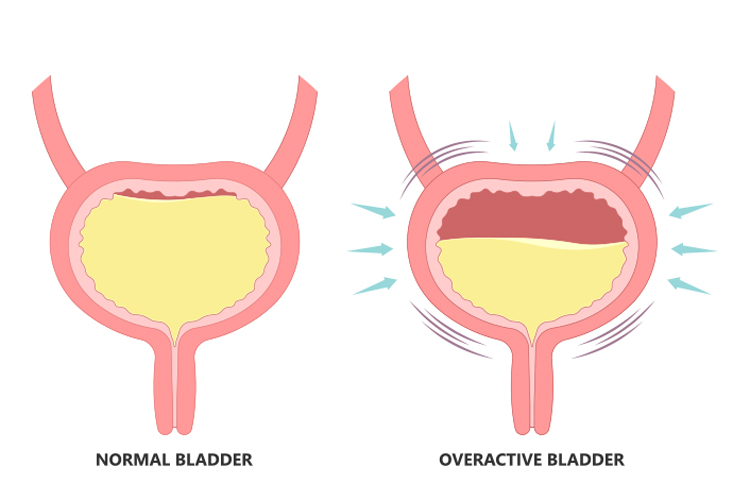
Multiple millions of individuals worldwide experience the complications of overactive bladder although healthcare systems neglect to focus on its prevalence. The condition results in multiple daily difficulties because it creates discomfort and embarrassment along with life-quality degradation. Early detection of overactive bladder depends on people understanding the symptoms that occur in this condition. Following these guidelines enables you to detect symptoms specifically in female patients as you move toward prompt medical care.
What is an Overactive Bladder?
The condition of overactive bladder causes light bladder leaks when patients experience abrupt and repeated bladder urges. The condition produces urgent needs to urinate which can activate nighttime accidents with urinary leakage. OAB serves as a medical symptom of other conditions which need proper examination.
Common Overactive Bladder Symptoms
The initial step for managing overactive bladder begins with detecting its symptoms. The most common symptoms include:
-
Frequent Urination
People who suffer from OAB will experience urination needs above eight times each day or multiple times during nighttime. The condition interferes with regular activities and disturbs the normal sleep schedule.
-
Urgency to Urinate
Pointing to an overactive bladder one can easily recognize this condition because it leads to urgent and powerful needs to use the restroom before delay is possible.
-
Urge Incontinence
Some patients experience involuntary urine leakage from a sudden need to urinate and are unable to make it to the bathroom at that exact moment.
-
Nocturia
Being required to urinate multiple times when resting at night is an OAB symptom that creates serious sleep interrupted patterns.
Overactive Bladder Symptoms in Females
The condition known as overactive bladder symptoms affects women more often than men because pregnancy along with menopause and hormonal changes create vulnerable risk factors. The symptoms which female patients commonly experience involve:
-
The pelvic region of women sometimes feels uncomfortable while they need to urinate often.
-
Female patients experience leakage due to physical activities such as exercise or coughing or laughing particularly after delivering a baby.
-
Hormonal changes in postmenopausal women lead to muscle weakening in the bladder which elevates their susceptibility to developing OAB symptoms.
Causes of Overactive Bladder
OAB development results from various causes which include:
-
Bladder muscles lose their strength naturally throughout ageing thus raising the chances of experiencing symptoms related to an overactive bladder.
-
A person's risk of OAB increases by neurological conditions that disrupt signals directing the bladder function including multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's disease and stroke.
-
Repeated urinary tract infections generate bladder irritation which results in symptoms of OAB.
-
The use of some medications like diuretics leads to greater urine volume production thereby intensifying symptoms of OAB.
Diagnosis of Overactive Bladder
A healthcare professional needs to evaluate your condition if you show symptoms of overactive bladder. The diagnosis usually involves:
-
The doctor will perform a medical history review that includes questioning about symptoms as well as medical background and daily practices.
-
During female examination doctors perform pelvic tests to discover potentially present abnormalities.
-
Your doctor can identify any urinary condition or infection through urine examinations.
-
By maintaining a bladder diary which records both fluid consumption and urination occasions as well as leakage incidents doctors can identify OAB.
Treatment Options for Overactive Bladder
The level of OAB symptom severity along with its root cause determines the necessary treatment approach. Common treatment options include:
-
Lifestyle Modifications
-
Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Practising bladder training techniques
-
Medications
Doctors usually provide anticholinergic or beta-3 agonist drugs to patients for bladder muscle relaxation as well as urgency control.
-
Pelvic Floor Exercises
The practice of Kegel exercises helps females enhance bladder control by strengthening pelvic muscles.
-
Nerve Stimulation
Extreme cases of bladder dysfunction respond to electrical nerve stimulation that controls bladder activity.
-
Surgery
Surgery becomes a treatment option for extraordinarily rare cases where doctors want to either boost bladder size or decrease nerve signals.
Coping with Overactive Bladder
The life quality of someone with overactive bladder symptoms will become better by implementing these valuable strategies:
-
To maintain further safety you should use absorbent pads
-
Using waterproof mattress covers
-
Accessing support groups helps people exchange narratives of their experiences.
-
Practising mindfulness and stress-reduction techniques
When to Seek Medical Help
People should obtain medical assistance when their symptoms of overactive bladder affect their daily functioning. Startling your condition early will stop secondary issues from occurring and help your total health condition.
Conclusion
Early diagnosis of overactive bladder depends on proper recognition of its warning signs. Professional healthcare assistance will direct you toward the most suitable treatment for your overactive bladder condition regardless of symptom severity. You can recover your bladder control while simultaneously improving your quality of life by applying correct methods. Your time has arrived to break free from the OAB control since taking action now leads you to healthier days.
Categories
Hernia Repair
Appendicitis
Piles
Urological Treatment
Hernia treatment
Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Gall Bladder Stone
Urinary / Kidney Stone
Vitamins
Indian Health Care System
Exercise
Obesity
Female Urinary Incontinence
Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery (SILS)
Kidney Cancer
Bladder Cancer
Ovarian cancer
Nephrology
Bariatric Surgery
Kidney Function Test
Female Urology
Radiation Therapy

