Piles Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment - Need to Know
2018-06-08 / RG STONE HOSPITAL / Urinary / Kidney Stone
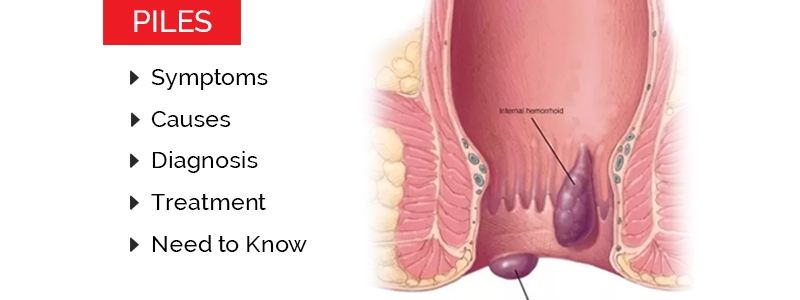
Haemorrhoids are vascular structures in the anal canal , which help with stool control. In their physiological state, they act as a cushion composed of arterio-venous channels and connective tissue that aid the passage of stool. They become pathological (piles) when swollen or inflamed. Piles are a very common ailment that may affect men or women at any age. These are caused due to continuous high pressure in the veins. Other causes include constipation, excessive straining during bowel movements and persistent diarrhoea. These swellings are usually round, discoloured, and small lumps. Some patients can feel these lumps on their anus or even hanging from the anal canal. A lot of times, these lumps can be very painful and even bleed due to any kind of damage. There are many types of piles treatment available which focuses on relieving the symptoms and bring in the much-needed relief.
Types of Piles
Piles are divided into two categories- internal piles and external piles.
As the name suggests, internal piles occur inside the anal canal, but they can also come out and hang outside your anus. This type of piles is further classified on the basis of whether they come out of the anus and if they do, how far are they out. They are classified as-
- First degree- This type of piles do not come out of the anus but might bleed
- Second degree- They come out during a bowel movement but then go inside later
- Third degree- They come out but will go inside if you push them
- Fourth degree- They are partially out of your anus and cannot be pushed inside. They can swell and can result in immense pain if blood clotting occurs inside the lump
External piles, on the other hand, occur close to the anus below the anal canal. They too can be painful if blood clots inside the lumps.
Piles symptoms
It is not necessary for piles to readily show any noteworthy symptoms. If there are symptoms, they might include-
- A lump around or in the anus
- Bleeding during the bowel movement
- Leaking faeces or slimy mucus discharge from the anus
- Feeling of constipation
- The skin around the anus feels sore or itchy
- In case of external piles, feeling of discomfort and pain after bowel movement
Diagnosing Piles
A general physician would examine you and ask you about the symptoms. A gloved finger is usually inserted into the anus to feel the rectum and presence of lumps. They might also use proctoscope to view the insides of the rectum.
?In some cases, the physician might also ask a patient to get a blood test done to know if you are suffering from anaemia, a condition where red blood cells are lower than normal. Anaemia might suggest that the piles problem is severe.
If the results suggest that the symptoms might be due to some other condition, the physician will recommend other tests.
Piles Treatment
In past, open surgery was the only option available. But today, with minimally invasive procedures, doctors approach for patient care has revolutionized. New procedure for haemorrhoids is called ‘Minimally Invasive Procedure for Haemorrhoids’ (MIPH), also called ‘Stapler Haemorrhoidectomy’.
? The technique uses a stapling device and takes advantage of the fact that pain-sensing nerve fibers are not present high up in the anal canal. In this procedure, the mucosa above the dentate line (containing part of pile mass) is excised and stapled with the stapler gun, thereby taking care of bleeding and prolapse. The pile masses are compressed into a cup like cavity inside the stapler. When fired, the titanium staples cut and seal simultaneously, causing minimal bleeding. As the cut line is above the nerves, there is less post-operative pain. Also, there is no incision on the perianal skin or lower part of anal canal and the wound in the anal mucosa is also primarily closed with a stapler, thus, there is no need to do any post-operative dressing. It is less painful and ensures early recovery.
Categories
Hernia Repair
Appendicitis
Piles
Urological Treatment
Hernia treatment
Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Gall Bladder Stone
Urinary / Kidney Stone
Vitamins
Indian Health Care System
Exercise
Obesity
Female Urinary Incontinence
Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery (SILS)
Kidney Cancer
Bladder Cancer
Ovarian cancer
Nephrology
Bariatric Surgery
Kidney Function Test
Female Urology
Radiation Therapy
Alcoholic Fatty Liver
Liver disease
Gastroenterology
Kidney Disease
Nutrition & Health
Lung Cancer

