Urinary tract infection – A guide for men
2025-04-07 / RG STONE HOSPITAL / Urological Treatment
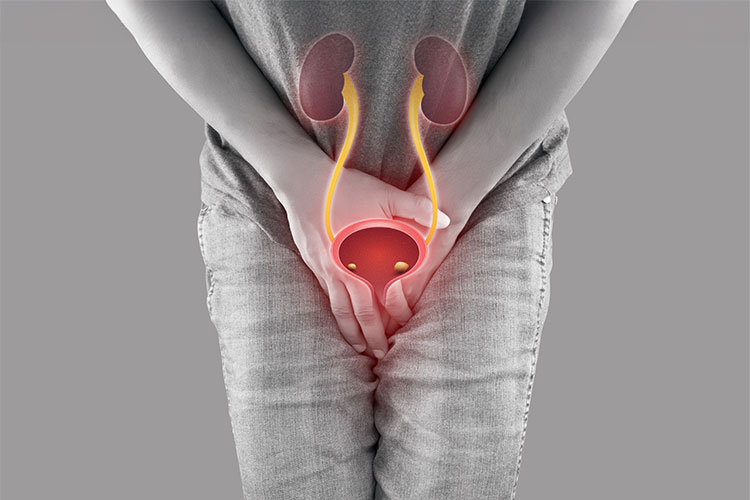
The urinary tract infection (UTI) represents a frequent bacterial disease which targets the bladder alongside the urethra and kidneys and ureters also. Urinary tract infection is more prevalent among females yet men may develop UTIs which tend to cause more serious health complications when doctors do not treat them. This article examines all aspects related to urinary tract infection specifically in male patients including their origins as well as symptoms and therapeutic approaches and prevention methods.
The Nature of Urinary Tract Infections Exists Specifically for Male Individuals
The urinary tract of men becomes infected by bacterial growth. The infection develops in different sections throughout the urinary tract system.
-
Urethritis – Infection in the urethra
-
Cystitis – Infection in the bladder
-
Pyelonephritis – Infection in the kidneys
Older men between 50 years of age face an increased risk of UTIs because of their urinary conditions which include swollen prostate and difficulty emptying the bladder.
Causes of Urinary Tract Infection for Men
Multiple elements increase a man's vulnerability to develop UTIs because of the following reasons:
-
Bacterial Entry: The entry point for UTI-causing bacteria is typically through the urethra where E. coli bacteria commonly act as the most frequent
-
bacterial cause of UTI infections.
-
Enlarged Prostate(BPH): An enlarged prostate condition under the classification of BPH blocks the normal flow of urine which raises the likelihood of infections.
-
Kidney Stones: The buildup of stones inside the kidney results in bacterial growth because of blocked urine passage.
-
Weakened Immune System: Conditions like diabetes increase vulnerability to infections.
-
Unprotected Sexual Activity: Acquiring STIs like chlamydia or gonorrhoea through unprotected sexual engagement causes UTI symptom reproduction.
-
Urinary Catheters: Bacteria enter the urinary tract through prolonged catheter usage as a urinary device.
Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection in Men
A urinary tract infection shows these signs among male individuals:
-
Frequent urge to urinate
-
Burning or pain during urination
-
Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
-
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
-
Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
-
Kidney infection will cause fever and chills to appear in your body.
-
Experiencing trouble when peeing together with incomplete bladder drainage
Medical care should be sought right away when any symptoms arise except for kidney complications.
Diagnosis and Treatment of UTI in Men
Diagnosis
Doctors diagnose UTIs through:
-
Urine Analysis – Checking for bacteria, white blood cells, or blood in the urine.
-
The medical test used for identifying which bacteria league causes the infection requires urine sample analysis.
-
The diagnosis of recurring UTIs includes ultrasound or CT Scan for detecting kidney blockages or potential problems.
Treatment
The physician selects antibiotics according to test results which identify the current bacterial strain.
These medications help reduce unwanted burning sensation together with uncomfortable symptoms.
Drinking plenty of water serves as an effective method for bacteria elimination through urine flushing.
The bladder becomes irritated when people avoid consuming caffeine, alcohol and spicy foods.
Men usually recover from UTIs without antibiotics after 7-14 days of standard medical treatment. Hospitalization accompanied by intravenous antibiotic administration becomes necessary when patients develop severe UTI symptoms.
Prevention Tips for Urinary Tract Infection in Men
Maintaining proper hydration requires men to drink at least eight glasses of water throughout each day.
Regular genital washing constitutes good hygiene practice.
After sexual intercourse urinating helps bacteria successfully wash away from the body.
Regular emptying of the bladder is crucial because urinary retention should be avoided.
Both alcohol and caffeine should be limited since they increase bladder sensitivity.
Medical professionals should treat both prostate problems and diabetes since they can form the basis for urinary tract infections.
Conclusion
The occurrence of urinary tract infections is not typical among men but such infections remain dangerous when treatment is delayed. Treatment soon after diagnosis proves critical to stopping UTI from spreading to kidneys or bloodstream. A healthcare specialist at RG Hospital can properly diagnose and create specific treatment plans when you exhibit symptoms of UTI.
Categories
Hernia Repair
Appendicitis
Piles
Urological Treatment
Hernia treatment
Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Gall Bladder Stone
Urinary / Kidney Stone
Vitamins
Indian Health Care System
Exercise
Obesity
Female Urinary Incontinence
Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery (SILS)
Kidney Cancer
Bladder Cancer
Ovarian cancer
Nephrology
Bariatric Surgery
Kidney Function Test
Female Urology
Radiation Therapy

