Why Is Benign Hyperplasia Treatment Necessary?
2024-09-30 / RG STONE HOSPITAL / Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
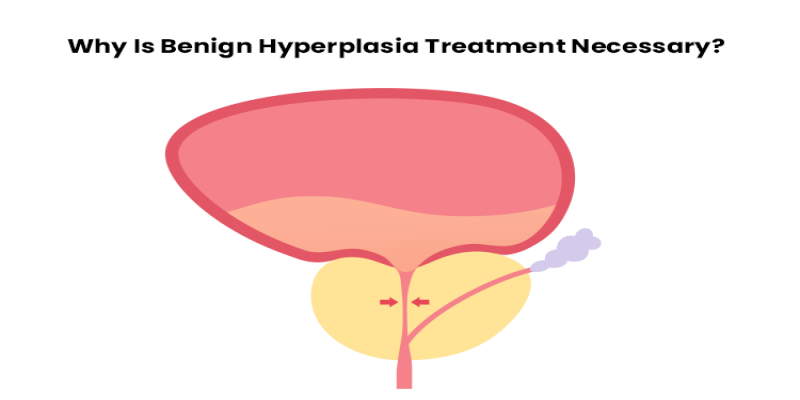
Introduction
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), commonly referred to as prostate gland enlargement, is a condition that affects many men as they age. Characterized by an increase in the size of the prostate gland, BPH can lead to various urinary symptoms that significantly impact a man's quality of life. While it is not cancerous, the condition can still cause considerable discomfort and complications if left untreated. This blog will delve into the reasons why treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia is necessary, explore the available treatment options, and highlight the importance of early intervention.
Understanding Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, which is located below the bladder and surrounds the urethra. The prostate plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system, primarily in the production of seminal fluid. As men age, hormonal changes can lead to an increase in prostate cells, resulting in an enlarged prostate.
While not everyone with an enlarged prostate will experience symptoms, many men do, and these can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms of BPH include:
-
Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia)
-
Urgency to urinate
-
Difficulty starting urination
-
Weak urine stream or a stream that stops and starts
-
Incomplete emptying of the bladder
Why Treatment Is Necessary
-
Quality of Life Concerns
The symptoms of BPH can severely affect a man's quality of life. Frequent trips to the bathroom, especially at night, can lead to disrupted sleep patterns and fatigue during the day. Difficulty in urination can also lead to embarrassment and anxiety, affecting social interactions and overall well-being. By seeking treatment, men can alleviate these symptoms and improve their daily life.
-
Risk of Complications
Untreated BPH can lead to various complications, including:
-
Bladder Stones: Incomplete emptying of the bladder can lead to the formation of stones.
-
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Urinary retention can increase the risk of infections.
-
Bladder Damage: Chronic urinary retention can weaken the bladder muscles, making it harder to empty completely.
-
Kidney Damage: In severe cases, pressure from the enlarged prostate can affect the kidneys, leading to potential kidney damage.
Addressing BPH early through appropriate treatment can help prevent these complications.
-
Psychological Impact
Living with the symptoms of BPH can take a toll on mental health. The constant worry about urinary issues can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression. Seeking treatment not only addresses the physical symptoms but also promotes better mental health by reducing stress and improving overall well-being.
-
Impact on Relationships
BPH symptoms can also affect personal relationships. Frequent urination and associated anxiety can hinder intimacy, leading to tension and frustration in relationships. By effectively managing the symptoms of BPH through treatment, men can restore their confidence and improve their relationships.
Treatment Options for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The treatment for BPH varies depending on the severity of the symptoms and the individual patient's health status. Here are some common treatment options:
-
Lifestyle Modifications
In mild cases, doctors may recommend lifestyle changes that can help manage symptoms, including:
-
Dietary Changes: Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake can minimize urinary urgency and frequency.
-
Fluid Management: Limiting fluid intake in the evening can reduce nighttime urination.
-
Bladder Training: This involves techniques to help the bladder hold more urine and decrease the urge to urinate.
-
Medications
Medications are often the first line of treatment for moderate to severe BPH symptoms. Commonly prescribed medications include:
-
Alpha Blockers: These medications relax the muscles around the prostate and bladder neck, making urination easier. Examples include tamsulosin (Flomax) and alfuzosin (Uroxatral).
-
5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors: These drugs help shrink the prostate by blocking the hormone that causes prostate growth. Finasteride (Proscar) and dutasteride (Avodart) are common examples.
-
Combination Therapy: Sometimes, a combination of alpha blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors is used for better results.
-
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For men who do not respond to medication or prefer not to take them, minimally invasive procedures may be recommended. These include:
-
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): This surgical procedure removes excess prostate tissue to relieve pressure on the urethra.
-
Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can reduce prostate size with minimal bleeding and a shorter recovery time.
-
UroLift Procedure: This technique involves placing small implants to lift and hold the enlarged prostate tissue out of the way, relieving pressure on the urethra.
-
Surgery
In cases of severe BPH, traditional surgical options may be necessary. The most common surgery for BPH is prostatectomy, which involves the removal of all or part of the prostate gland. This option is usually considered when other treatments have failed or if there are significant complications.
Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention in treating benign prostatic hyperplasia is crucial for several reasons:
-
Symptom Management: Early treatment can help manage symptoms effectively, preventing them from worsening over time.
-
Prevention of Complications: Addressing BPH symptoms early can reduce the risk of complications, such as urinary tract infections and kidney damage.
-
Improved Quality of Life: Prompt treatment can lead to an immediate improvement in quality of life, allowing men to engage fully in their daily activities without the burden of urinary symptoms.
Conclusion
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a common condition that can significantly affect men's health and quality of life. While it is not life-threatening, the symptoms associated with BPH can lead to various complications if left untreated. Seeking timely treatment is essential to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve overall well-being. With a range of treatment options available, including lifestyle modifications, medications, minimally invasive procedures, and surgery, men have the opportunity to manage their condition effectively. If you are experiencing symptoms of BPH, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Remember, addressing your health is the first step towards a better quality of life!
Categories
Hernia Repair
Appendicitis
Piles
Urological Treatment
Hernia treatment
Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Gall Bladder Stone
Urinary / Kidney Stone
Vitamins
Indian Health Care System
Exercise
Obesity
Female Urinary Incontinence
Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery (SILS)
Kidney Cancer
Bladder Cancer
Ovarian cancer
Nephrology
Bariatric Surgery
Kidney Function Test
Female Urology
Radiation Therapy
Alcoholic Fatty Liver
Liver disease
Gastroenterology
Kidney Disease

